Glossary and Abbreviations
Understanding PF Terminology
Pulmonary fibrosis is a complex family of diseases, and it easy to get overwhelmed with the terms and abbreviations that are often used to describe a patient’s condition. We hope that this list of terms and abbreviations helps you better understand some of the language used to describe your diagnosis and better communicate with your care team. Remember: If there’s something you don’t understand about your diagnosis, ask your provider!
Glossary
Acute exacerbation: An episode of rapid worsening of a pulmonary (relating to lungs) condition.
Alveoli: Tiny air sacs in the lungs where carbon dioxide leaves the bloodstream and oxygen enters the bloodstream.
Biopsy: An examination of living tissue to discover the presence or extent of disease. During a lung biopsy, a very small piece of tissue is taken.
Bronchial tree: The series of airways connecting the trachea (windpipe) to the alveoli.
Bronchus: One of the airways of the bronchial tree (plural: bronchi).
Bronchoscope: A tool usually passed through the nose or mouth used for inspecting the inside of airways (bronchial tubes) of the lungs. Biopsies of the lungs can be performed by bronchoscopy.
Chest X-ray: An X-ray that produces images of the heart, lungs, airways, and blood vessels, as well as the bones of the spine and chest. A PA/lateral chest X-ray provides a two-dimensional view of the lungs.
Comorbidity: A disease or other medical problem that occurs simultaneously with PF. A comorbidity is typically neither a cause nor a consequence of pulmonary fibrosis.
Contraindications: Specific situations in which a drug or procedure should not be used because it may be harmful to the person. An absolute contraindication means use of the drug or procedure could cause a life-threatening situation. A relative contraindication means the benefits may outweigh the risk, but caution should be used.
Connective tissue disease-related interstitial lung disease (CTD-ILD): Lung disease that may develop in some people with a connective tissue disease (also known as rheumatologic, collagen vascular, or autoimmune diseases) such as scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis, Sjogren’s syndrome, systemic lupus erythematosus, polymyositis, or dermatomyositis. CTD-ILD causes inflammation and fibrosis of the lungs. Some patients with ILD may have features of a CTD, but not meet all of the criteria necessary to diagnosis a specific autoimmune disease.
Computed tomography (CT) scan: A procedure that uses a combination of X-rays and a computer to create a three-dimensional image of an individual’s organs, bones, and other tissues. A CT scan shows more detail than a regular X-ray and is sometimes referred to as a CAT scan.
Diffuse parenchymal lung diseases (DPLD): Another name for interstitial lung diseases.
Diffusion capacity (DLCO): A measure of the ability of gases to diffuse into the bloodstream.
Dyspnea: Difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, or breathlessness.
Exacerbation: An episode of rapid decline or the emergence of more severe symptoms.
Fibroproliferation: The growth of fibroblasts, the cells that make scar tissue.
Fibrosis: Scar tissue.
Forced expiratory volume (FEV1): The amount of air you can blow out in one second after filling up your lungs with as much air as possible. Measured by a test called spirometry.
Forced vital capacity (FVC): The amount of air you can blow out of your lungs seconds after filling up your lungs with as much air as possible. Measured by a test called spirometry.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): A medical condition defined by passage of stomach contents into the esophagus (food pipe) and often into the throat. GERD can cause discomfort (“heartburn” or “acid indigestion”) and sometimes injures the lining of the esophagus. Also called acid reflux disease.
Hospice care: Focuses on caring, not curing, with an emphasis on comfort and support for patients. Hospice is designated for patients with a life expectancy of six months or less certified by a physician.
Hypoxemia: A below-normal level of oxygen in the blood.
Idiopathic: Of unknown cause.
Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP): A family of 9 types of ILD of unknown cause.
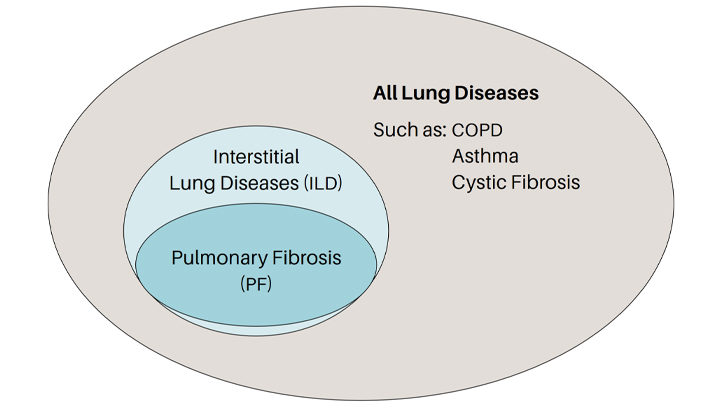
Interstitial lung diseases (ILD): A broad category of over 200 lung diseases that affect the lung interstitium. Typically, ILDs cause inflammation, fibrosis (scarring), or an accumulation of cells in the lung not due to infection or cancer.
Interstitium: The walls of the air sacs of the lung. Your lung is made of air, interstitium, and blood vessels.
Palliative care: Non-curative therapy that treats symptoms and focuses on improving quality of life. It can be received at the same time as curative therapy.
Pathologist: A physician specializing in disease-associated changes in tissue and organs. Pathologists aid in making a medical diagnosis.
Pulmonary: Relating to the lungs.
Pulmonary hypertension (PH): Abnormally high blood pressure in the pulmonary (lung) arteries, which connect the heart to the lungs. Pulmonary hypertension is sometimes called pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH).
Pulmonologist: A physician specializing in the lungs.
Radiologist: A physician specializing in using radiology tests (e.g., X-rays) to diagnose illness.
Rheumatologist: A physician specializing in rheumatic diseases, which may include autoimmune diseases and joint diseases.
Spirometry: A test that measures the amount of air inhaled and exhaled with each breath.
Usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP): A specific abnormal radiologic or pathologic pattern of interstitial lung disease.
Abbreviations
AIP: acute interstitial pneumonia
CAT: computed axial tomography
CT: computed tomography
CTD-ILD: connective tissue disease interstitial lung disease
DLCO: diffusion capacity
DPLD: diffuse parenchymal lung disease
FPF: familial pulmonary fibrosis
FEV: forced expiratory volume
FVC: forced vital capacity
GERD: gastroesophageal reflux disease
HFO: High-flow oxygen
HRCT: high-resolution computed tomography
IIP: idiopathic interstitial pneumonia
ILD: interstitial lung disease
IPF: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
LPM: liters per minute
NSIP: non-specific interstitial pneumonia
OSA: obstructive sleep apnea
PAH: pulmonary arterial hypertension
PH: pulmonary hypertension
PF: pulmonary fibrosis
PFTs: pulmonary function tests
POC: Portable oxygen concentrator
PR: Pulmonary rehabilitation
RA-ILD: rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease
SSc-ILD: scleroderma-associated interstitial lung disease
TLC: total lung capacity
UIP: usual interstitial pneumonia
VATS: video-assisted thoracoscopy surgery
